

‘Act East Policy’ announced in November 2014 is the upgrade of the “Look East Policy”.
The objective of ‘Act East Policy’ is to promote economic cooperation, and cultural ties and develop strategic relationships with countries in the Asia-Pacific region by providing enhanced connectivity to the States of the North Eastern Region including Arunachal Pradesh with other countries in our neighborhood.
Act East Policy provides an interface between North-Eastern India including the state of Arunachal Pradesh and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) region.
Act East Policy focuses on ASEAN countries + Economic Integration + East Asian countries + Security cooperation.
The 4C’s of Act East Policy:
The Assam Government has opened the Act East Policy Department to ensure the implementation of the Act East Policy in a time-bound manner. The Act East Policy Department will facilitate an environment for investment and rapid industrialization in the state.
👉 Which year are YOU targeting for success in the IAS/IPS/IFS Exam? 🚀
Table of Contents
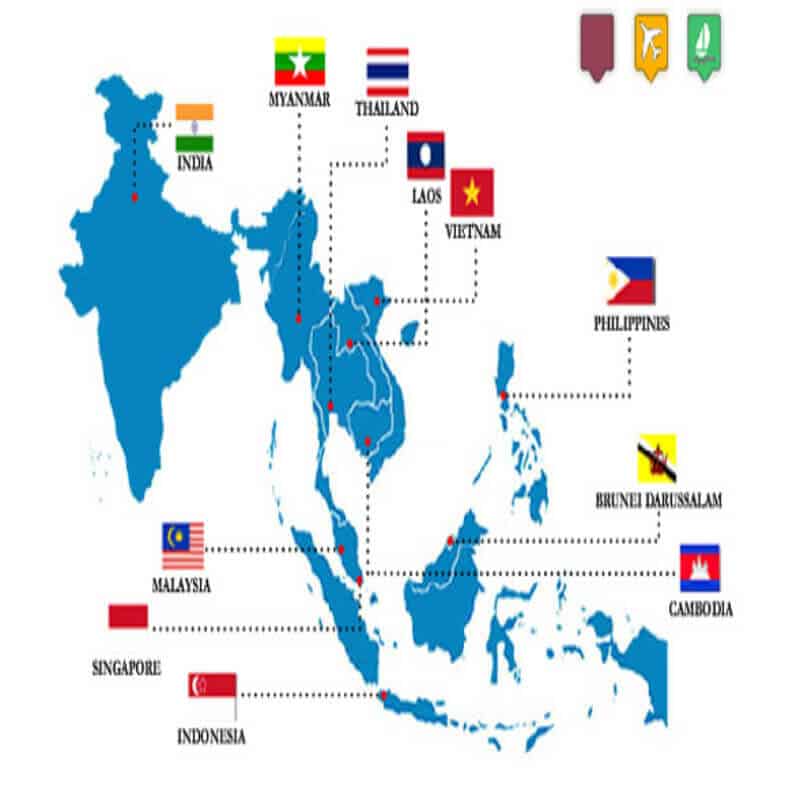
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN, was established on 8 August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand, with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration) by the Founding Fathers of ASEAN, namely Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand. Brunei Darussalam then joined on 7 January 1984, Vietnam on 28 July 1995, Lao PDR and Myanmar on 23 July 1997, and Cambodia on 30 April 1999, making up what is today the ten Member States of ASEAN.
SIMBEX: Singapore-India Maritime Bilateral Exercise, which has been held annually since 1994.
MILAN-Multi Nation Exercise, which takes place biennially between the navies of India, Singapore, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Thailand, Brunei, and Indonesia.
Kaladan Multimodal Transit Transport Project: This project is an important limb of the Act East policy and provides India with crucial access to the region.
Protocol on Inland Water Transit and Trade (PIWT&T):
For the use of Chattogram and Mongla Ports of Bangladesh for the movement of goods to and from India, the Memorandum of Understanding, dated and Standard Operating Procedure, has been finalized.
Comprehensive Project for Development of National Waterway (NW)-2:
Comprehensive Project for the development of NW-16&IBP route:
Assam: Construction of floating terminals on NW-2 and NW-16
Manipur: Loktak Inland Waterways Improvement Project for Loktak Lake
Mizoram: Development of IWT on river Khawthlangtuipui- Tuichawng in Lunglei District.
Tripura: Setting up of linkage with Meghna river system in Bangladesh by developing Gumti River.
All the above projects aim to comprehensively develop the northeast region and as well as boost India’s Act East policy by extending the connectivity and trade eastwards.
The India-Japan Act East Forum was established in 2017 to provide a platform for India-Japan collaboration in the North Eastern Region under India’s Act East Policy and Japan’s vision for a Free and Open Indo-Pacific.
India and Japan held the sixth joint meeting of the India-Japan Act East Forum (AEF) on 15 March 2022 in New Delhi.
They reviewed the progress of ongoing projects in various areas including connectivity, hydropower, forest management, water supply and sewerage, skill development, and Japanese language education.
The growing Chinese influence in the southeastern region and Indian Ocean region is a major factor pushing for the strengthening of the Act East policy. As security is an important aspect of the policy, it will aid in securing freedom of navigation and the rule of law in the Indo-Pacific region.
India’s involvement with QUAD is also an extension of achieving this security in the Indo-Pacific region.
The end of the Cold War and the subsequent rise of China have significantly altered the nature of Indo-ASEAN relations but the relations can be expected to strengthen further through economic linkages and security cooperation.
For India, the Act East policy seeks to fulfill its long-term developmental goals for its North Eastern region and to open up an additional avenue to accelerate its economic growth to counter China’s rising aggression in South Asia.
The Act East policy is seeking regional cooperation with ASEAN which provides India with a counterweight to potentially keep a check on an increasingly assertive China that seeks regional domination in Asia.
India needs to continue with stepped-up efforts to forge closer partnerships with concerned regional and Multilateral organizations such as ASEAN, ASEAN Regional Forum, East Asia Summit, BIMSTEC, Asia Cooperation Dialogue, Mekong Ganga Cooperation, and Indian Ocean Rim Association.
On the cultural front, Buddhist and Hindu links could be energized to develop new contacts and connectivity between people.
On connectivity, special efforts should be made to develop a coherent strategy, particularly for linking ASEAN with our North East which is aimed to be achieved through the act east policy.